CNC Cutting Speed: Definition, Key Factors, and Its Impact on Tool Life

What is Cutting Speed?
切削速度是CNC加工中最核心的參數,指的是刀具切削刃與工件表面接觸時的相對線速度,通常以 每分鐘米數(m/min)或每分鐘英尺數(ft/min) 表示。對於 CNC 加工業者來說,切削速度的設定直接影響加工效率、表面品質與刀具壽命。若切削速度不正確,可能導致工件表面粗糙、刀具過快磨損,甚至造成加工失敗。因此,正確掌握 CNC 切削速度的定義,是提升產能與確保加工品質的首要條件。

Basic Formulas: Cutting Speed, Feed Rate, and Depth of Cut
Three fundamental parameters determine machining performance: cutting speed (Vc), feed rate (f), and depth of cut (ap). Their basic formulas are:
Cutting Speed Vc = (π × D × n) ÷ 1000
(D = tool diameter, n = spindle speed in RPM)
Feed Rate f = fz × z × n
(fz = feed per tooth, z = number of teeth)
切削深度ap為切削刀具一次切削進入工件的厚度。
Example 1: High-Speed Cutting of Aluminum Alloy
Tool: Ø20 mm carbide end mill, 4 flutes
Spindle Speed (n): 12,000 RPM
Feed per Tooth (fz): 0.05 mm/tooth
Depth of Cut (ap): 2 mm
Calculation:
Cutting Speed Vc = (π × D × n) ÷ 1000
= (3.14 × 20 × 12000) ÷ 1000
= 754 m/min
Feed Rate f = fz × z × n
= 0.05 × 4 × 12000
= 2400 mm/min
Depth of Cut ap = 2 mm
Suitable for high-speed machining of aluminum alloys, ensuring high productivity.
Example 2: Stable Cutting of Stainless Steel
Tool: Ø10 mm carbide end mill, 2 flutes
Spindle Speed (n): 3000 RPM
Spindle Speed (n): 3000 RPM Feed per Tooth (fz): 0.03 mm/tooth
Depth of Cut (ap): 1.5 mm
Calculation:
Cutting Speed Vc = (3.14 × 10 × 3000) ÷ 1000
= 94 m/min
Feed Rate f = 0.03 × 2 × 3000
= 180 mm/min
Depth of Cut ap = 1.5 mm
Suitable for medium-speed cutting of stainless steel, minimizing tool wear.
Example 3: Heavy Cutting of Mold Steel
刀具:Ø50 mm Face milling cutter,6刃
Spindle Speed (n): 600 RPM
Feed per Tooth (fz): 0.08 mm/tooth
Depth of Cut (ap): 3 mm
Calculation:
Cutting Speed Vc = (3.14 × 50 × 600) ÷ 1000
= 94 m/min
Feed Rate f = 0.08 × 6 × 600
= 288 mm/min
Depth of Cut ap = 3 mm
Suitable for low-speed, heavy-load cutting of mold steel, balancing stability and tool life.
These formulas are simple, but achieving both efficiency and extended tool life requires careful adjustment according to tool type, workpiece material, and machine stability.
Key Factors Affecting CNC Cutting Speed
Several conditions influence the selection of cutting speed:
Workpiece Material: Aluminum allows high-speed cutting, while stainless steel or hardened steel requires slower cutting speeds.
Tool Type: Carbide tools withstand higher cutting speeds compared to HSS tools.
Cutting Depth and Feed Rate: Larger engagement increases load, requiring reduced speed to protect tool life.
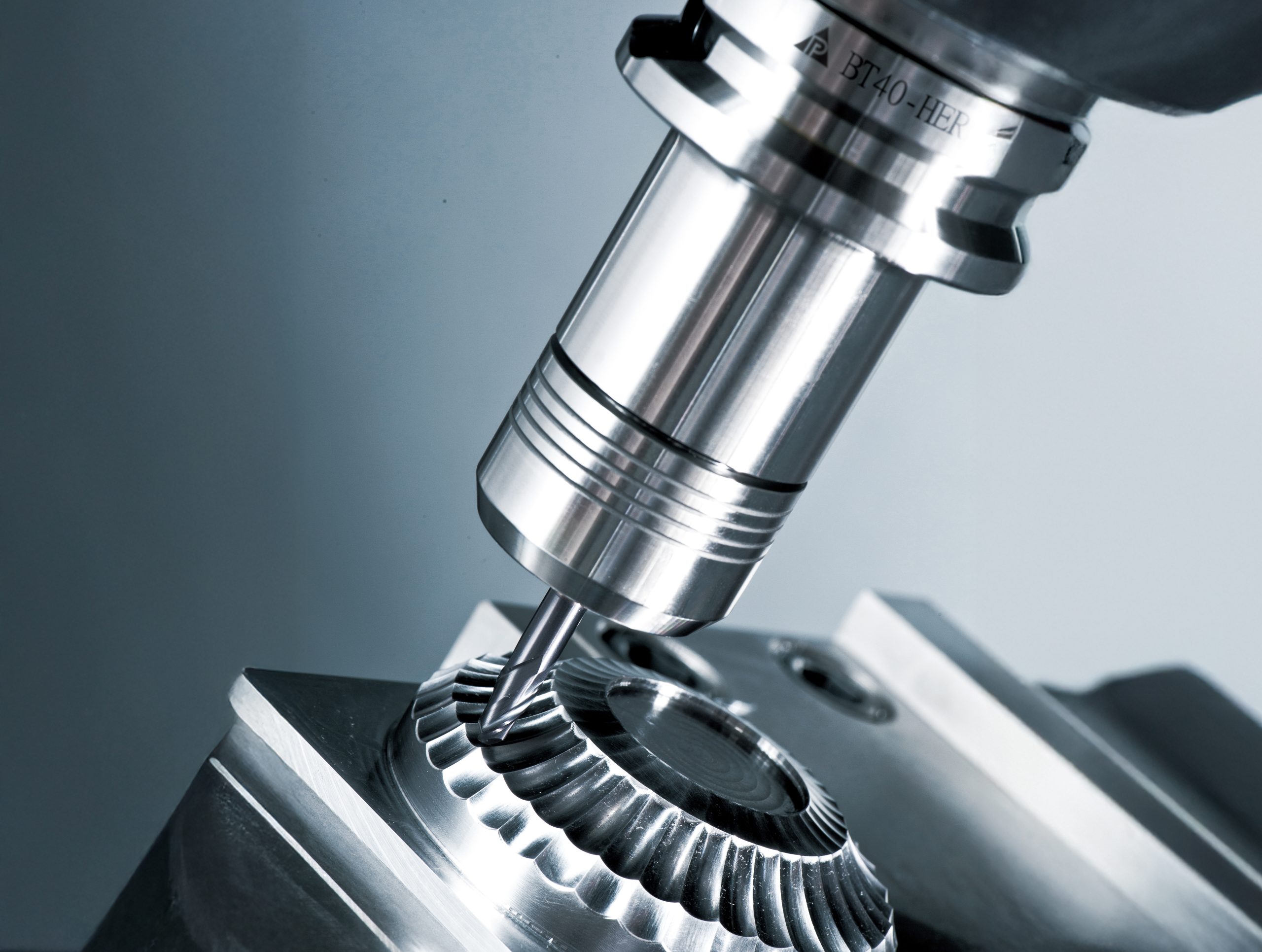
機台條件與刀桿穩定性:若Tool holder剛性不足,容易引起震動,造成刀具磨損與加工精度下降。
Therefore, CNC cutting speed should always be optimized according to real machining conditions rather than simply “faster is better.”

Practical Applications of Cutting Speed
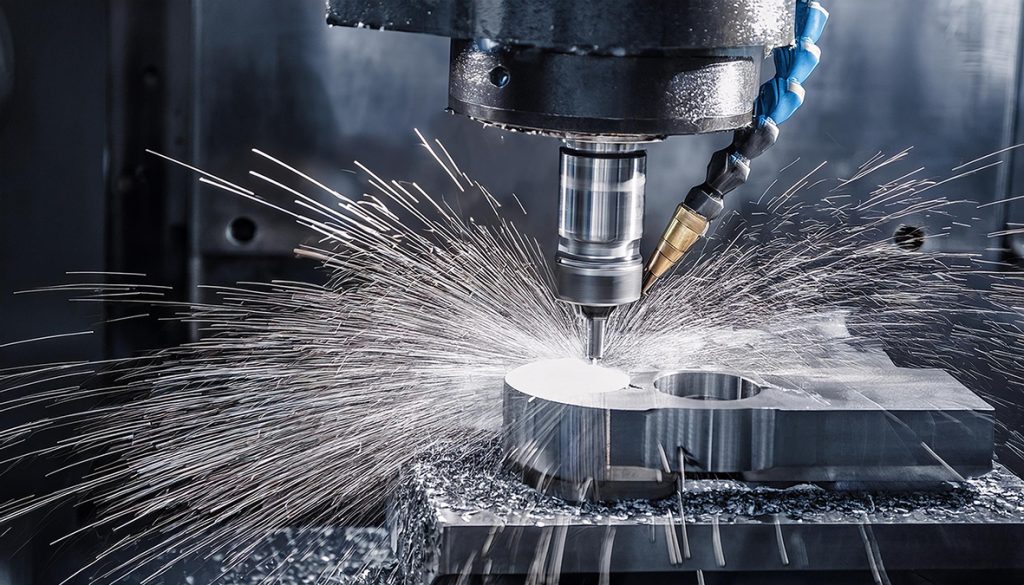
For instance, when machining aluminum alloys with a Ø20mm carbide end mill, cutting speeds can exceed 300 m/min to achieve high efficiency. In contrast, stainless steel or tool steel typically requires cutting speeds in the range of 80–150 m/min to minimize tool wear. In cases involving thin-wall parts or long tool overhangs, cutting speeds should be reduced, and a high-rigidity tool holder should be used to suppress vibration and maintain dimensional accuracy.
CNC Cutting Speed and Tool Life
In CNC machining, cutting speed has a significant impact on tool life. Excessive speed causes the cutting edge to wear rapidly due to high-temperature friction, while overly slow speed may lead to chip buildup, work hardening, and reduced efficiency. The optimal CNC cutting speed should strike a balance between efficiency and tool life.
To maintain stability and precision under high-speed machining, we recommend using the PARFAITE HER collet high-rigidity tool holder. With excellent dynamic balance and strong clamping force, PARFAITE tool holders effectively extend tool life, making them particularly suitable for high-speed machining, deep cavity milling, and precision component manufacturing. For CNC manufacturers, selecting the right tool holder along with proper cutting speed is the best solution to improve machining performance and ensure product quality.