What are the differences between SK-BT-ISO-CAT tool handle (tool holder) systems? - Tool handle handle part
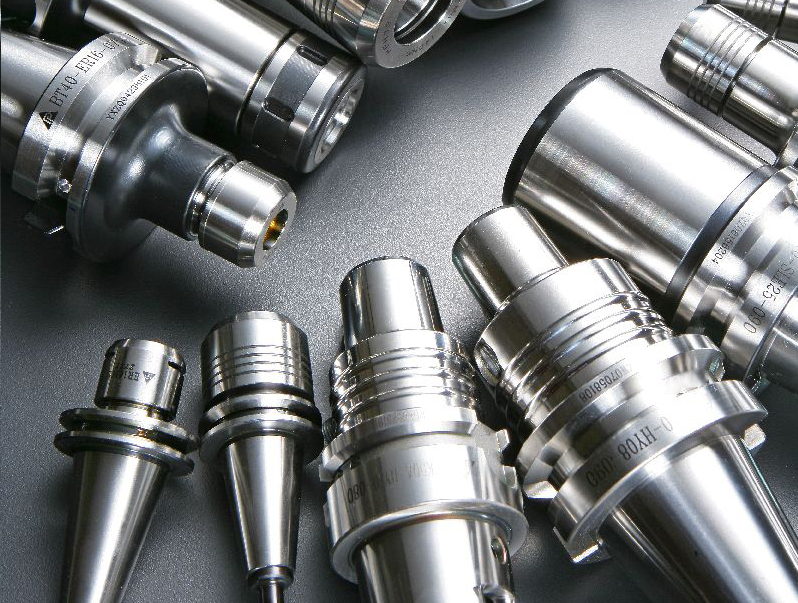

There are five common standards and specifications for tool holders with a taper of 7:24:
1. International standard ISO 7388 (referred to as ISO)
2. Japanese standard JIS B6339 (BT )
3. German standard DIN 2080 (NT or ST)
4. American standard ANSI/ASME B5.50 (CAT )
5. DIN 69871 (SK)
The NT type tool holder is tightened by a pull rod on a traditional machine tool, also known as ST tool holder; the other four (SK-BT-CAP-ISO) tool holders are tightened on the machining center through a rivet at the end of the tool holder. The handle is tightened.
There are various types of tool holders. Under the norms and principles established by each country, the tool holders are installed on the processing machine and closely combined with the cutting tools to create ever-changing metal processing art. From the Japanese standard BT (JIS B6339 & ISO7388X), the German standard SK (DIN 69871 & ISO 7388), the international standard HSK (ISO 12164), the American standard CAT (ANSI/ASME B5.50), etc., the differences in national standards have created a large number of Regional market demand. Looking at the above-mentioned international standards, except for the HSK series, BT, CAT, SK, and ISO are all 7:24 slope series. The 7:24 slope series can quickly clamp tools and has more general manufacturing technology. The cost is relatively low, but the industry is still evolving and progressing. However, in the 7:24 slope series, the inner hole at the front end of the spindle will expand under high-speed rotation, causing axial and radial dimensional changes, resulting in poor repeat positioning accuracy. Stability is a characteristic of the 7:24 slope series.
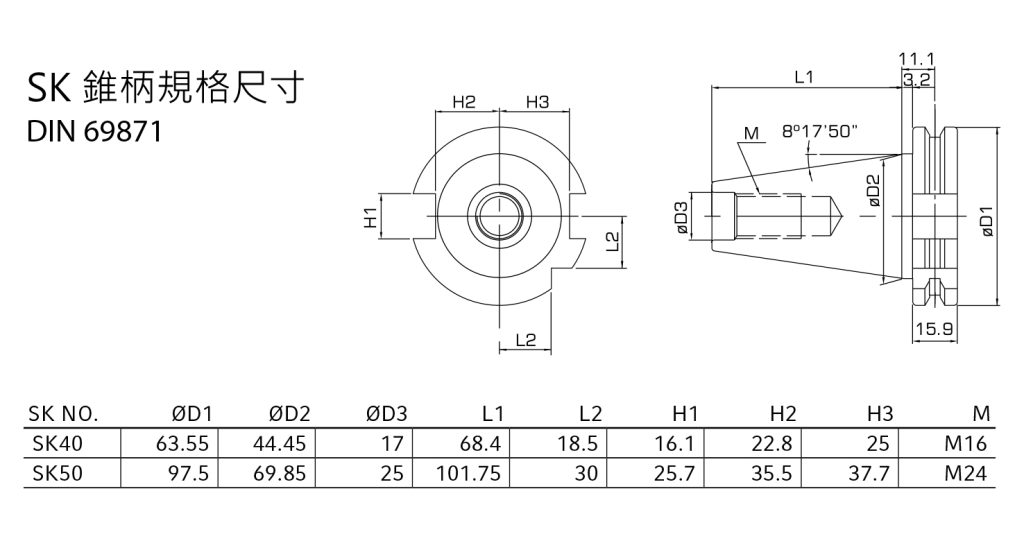
Specification and introduction of SK Tool handle
German standard DIN 69871-1: 1995 (No. 30, 40, 45, 50 and 60 tool taper shanks) 7:24 tool taper shanks for automatic tool changing machines are divided into type A and type AD in the German standard DIN 69871-1 There are three types of type AF: type A has a threaded bottom hole that is blocked; type AD has a threaded bottom hole that runs through; and type AF has a flange end face that provides water. The original German standard DIN 69893-1:1996 has been replaced by the new standard DIN 69873-1:2011. The new German standard also adopts the contents of the international standard ISO 12164-1:2001.
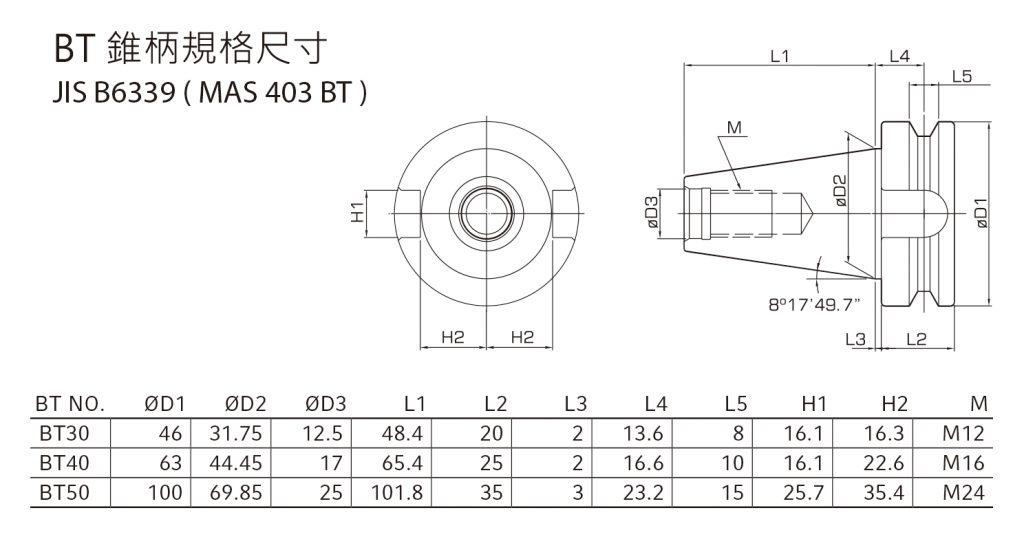
Specification and introduction of BT Tool handle
The current Japanese standard is JIS B 6339: 2011 (30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55 and 60 tool taper shanks), which is used to replace the Japan Machinery Machinery Industry Association standard MAS-403: 1975 (40, 45, 50 and No. 60 tool taper shank); although the Japanese standard JIS B 6339:2011 for 7:24 tool taper shank for automatic tool changing machine tools has replaced the Japan Machinery Machinery Industry Association standard MAS-403:1975, due to the same main external dimensions, It has basically no impact on use, so many manufacturers' samples are still marked with the MAS-403 standard code instead of JIS B 6339. The tool taper shank is codenamed "BT", and its characteristics are: the flange thickness is large; the V-shaped groove is asymmetrically distributed, close to the side of the working part; the two end keyways are symmetrically distributed; the end keyway is not milled through.
There are three types of rivets according to Japanese standard JIS B 6339:2011. The tensioning surface angle of the rivets is 45°60°90°. They are used for tensioning devices without steel balls and are code-named "PxxT". Among them, rivets are also available in models without central water outlet and with center water outlet.
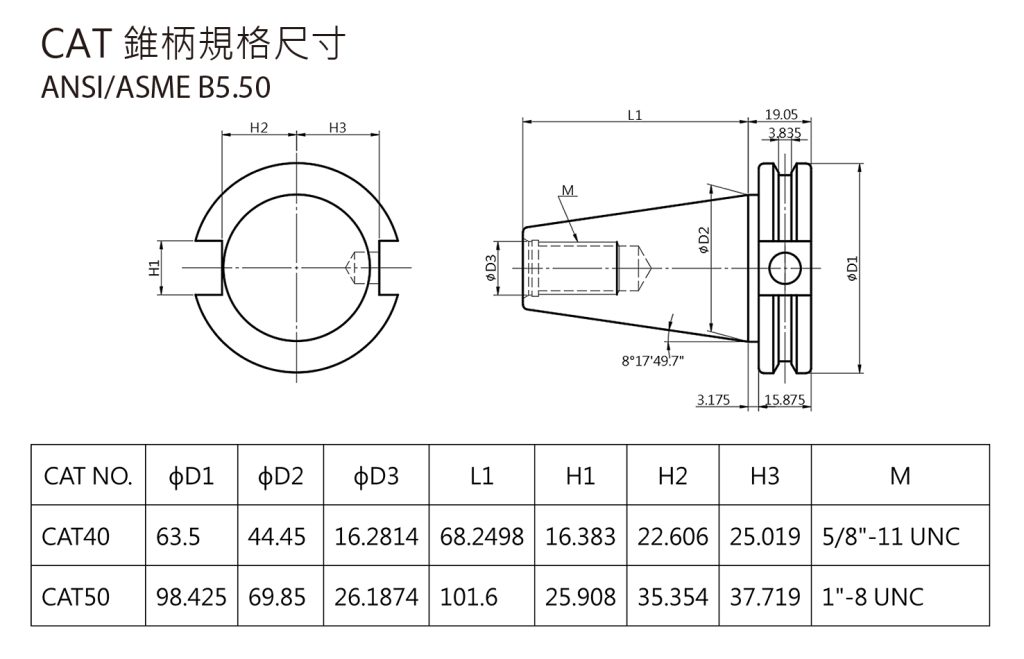
Specification and introduction of CAP Tool handle
The current American standard is AMSE B5.50-2015 (30, 40, 45, 50 and 60 tool taper shanks), which is used to replace the ANSI/AMSE B5.50-1985 standard. The American standard AMSE B5.50-2015 for 7:24 tool taper shanks for automatic tool changing machines has replaced ANSI/AMSE B5.50-1985. Similarly, because the external dimensions are the same, many manufacturers still mark ANSI/AMSE on their samples. B5.50, or just mark AMSE. Although the tool taper shank code is not specified in the standard, it is usually called "CAT". Its characteristics are: the flange thickness is small; the two end keyways are asymmetrically distributed; an identification hole is drilled on the bottom surface of one end keyway , used for tool positioning.
There is only one type of rivet in the American standard AMSE B5.50-1994. The tensioning surface of the rivet has a bevel angle of 45°, and there is no centering cylinder between the flange and the thread.
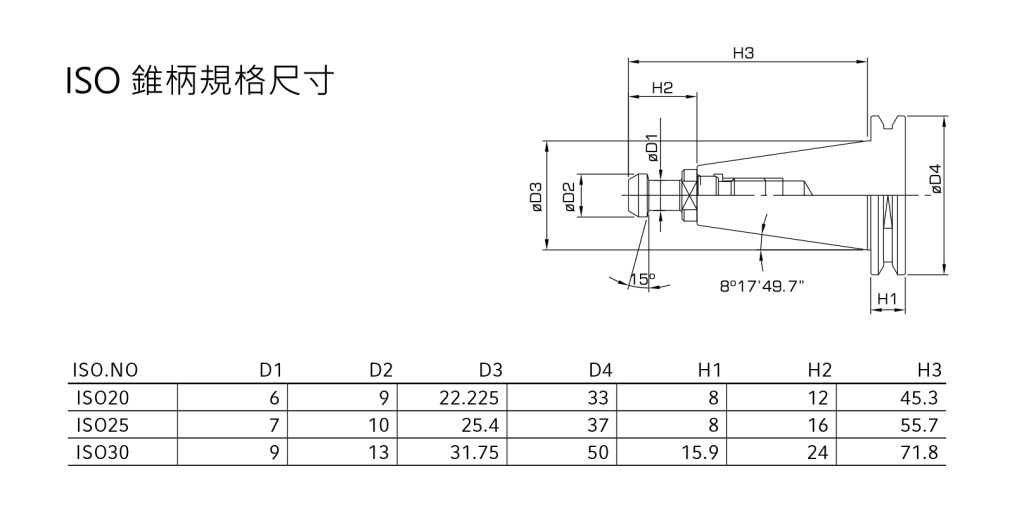
Specifications and introduction to ISO Tool handle
One of the universal tool holders with an ISO tool holder taper of 7:24, which is based on the international standard ISO7388. The installation dimensions of the ISO 7388 tool holder are no different from those of the DIN 69871 type. However, since the flange value of the ISO 7388 tool holder is smaller than that of the DIN 69871 tool holder, the ISO 7388 tool holder is installed on the DIN 69871 tapered hole. There is no problem on the machine tool, but if the DIN 69871 tool holder is installed on the ISO 7388 machine tool, interference may occur. The more common specifications of ISO tool holders at present: such as ISO20, 25, and 30, which are mostly used in small diameter and high-speed processing fields.
What are the differences between SK, BT, ISO and CAT Tool handle systems?
Although SK, BT, CAT, and ISO tool holders all belong to the 7:24 slope series, they have different specifications and size standards for flange surfaces, V-grooves, and keyways, and they all have their own unique advantages and application fields. Application scenarios. Understanding these differences can help users choose the most suitable tool holder system and improve processing efficiency and accuracy. With the continuous advancement of industrial technology, these tool handle systems will continue to be developed and optimized to meet the growing market demand. Finally, we briefly summarize the differences and comparisons between these four knife handles:
SK toolholder system (DIN 69871)
- standard: According to German standard DIN 69871.
- feature: There are three structures: A type, AD type and AF type, suitable for automatic tool changing machine tools.
- application: Widely used in German and European markets.
BT tool handle system (JIS B6339)
- standard: Based on the Japanese standard of JIS B6339, compatible with the MAS-403 standard.
- feature: The flange is thicker, the V-shaped grooves are asymmetrically distributed, and the two end keyways are symmetrically distributed.
- application: Mainly used in Japan and Asian markets, suitable for high-precision and high-stability processing requirements.
CAT tool holder system (ANSI/ASME B5.50)
- standard: Based on the American standard ANSI/ASME B5.50.
- feature: The flange thickness is small, the two end keyways are asymmetrically distributed, and there are identification holes for positioning.
- application: Widely used in the United States and North America markets, suitable for various automatic tool changing machine tools.
ISO Tool Holder System (ISO 7388)
- standard: Based on the international standard ISO 7388.
- feature: The installation dimensions are similar to DIN 69871, but the flange value is smaller, suitable for machine tools of different standards.
- application: Internationally applicable, suitable for various machine tools, especially in small diameter and high speed processing.
To learn more, please go to the official website:Precision tool holder selection SK series / ISO series selection