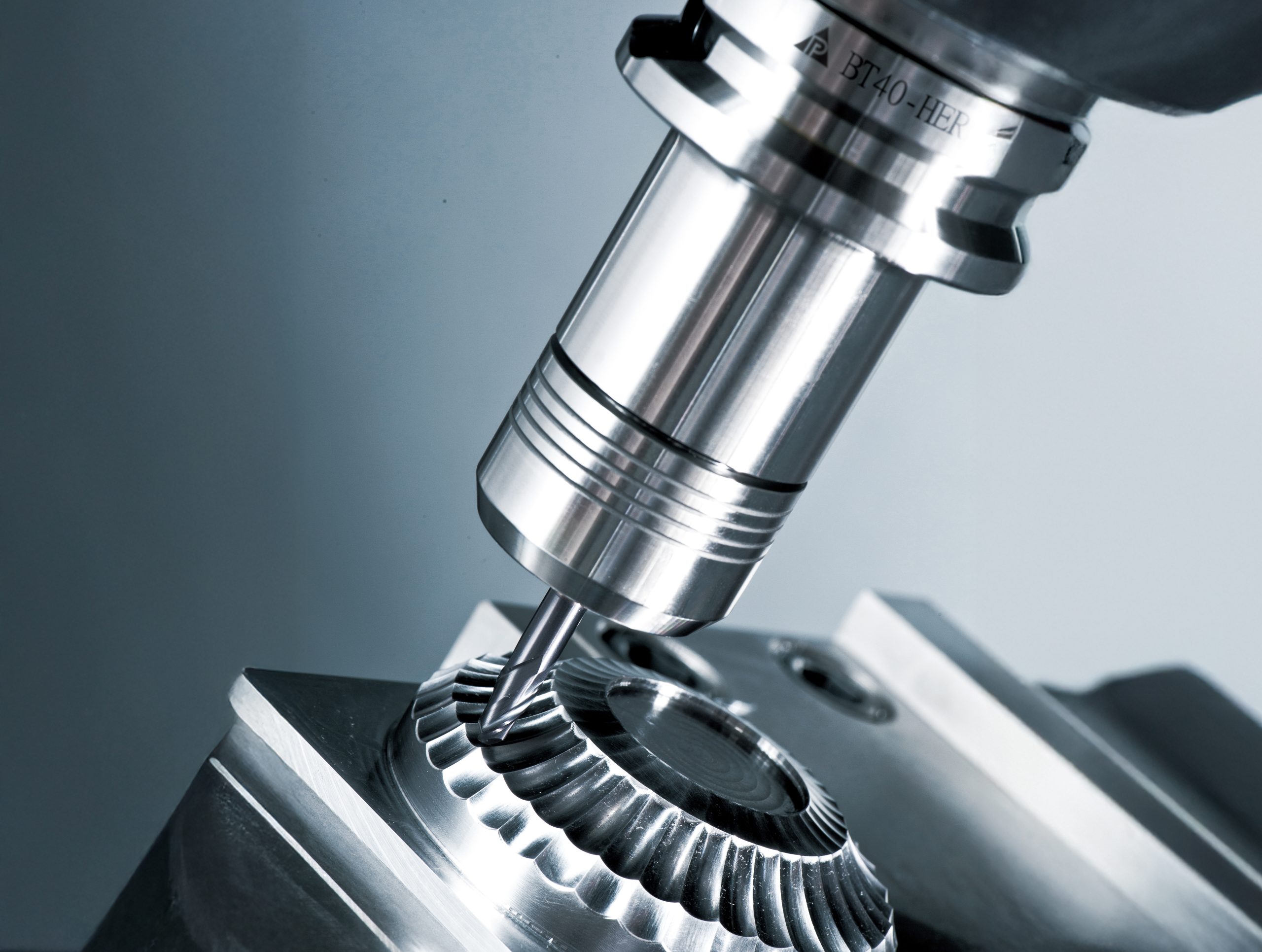
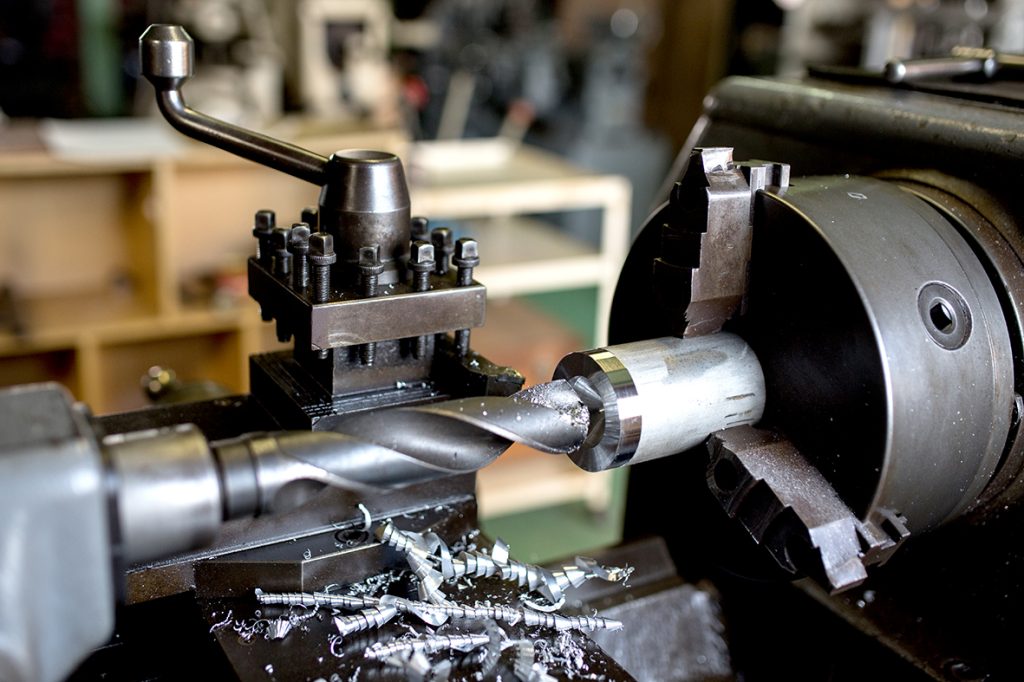
A Morse taper tool holder utilizes the principle of the Morse taper (MT) to securely fix cutting tools into the machine spindle or tailstock through frictional force between the tapered surfaces. This design provides excellent self-locking capability, allowing the tool holder to withstand substantial axial and radial loads during machining while maintaining high precision. Originally developed for connecting drill spindles to drill bits, Morse taper tool holders have since been widely adopted in various machine tools including lathes, milling machines, and vertical drilling machines, serving as a reliable and practical tool clamping system.
What is a Morse Taper?
The Morse taper is a standardized form of tool taper interface used to clamp cutting tools in machine tool spindles. It features a hollow tapered spindle that transmits torque to the tool shank through static friction. Morse tapers range from MT0 to MT7 in size, with MT2, MT3, and MT4 being the most common, especially in small to medium-sized machine tools. Each taper has an angle of approximately 1°26′, complying with ISO 296 and DIN 228 standards.

Features of Morse Tapers
1.Taper Standard: The taper ratio is approximately 1:20 (meaning the diameter increases by about 5 mm every 100 mm in length).
Small sizes (MT1 to MT2): Commonly used in small lathes, drilling machines, precision machining, or for light-duty tools such as small drills and tailstock centers.
Medium sizes (MT3 to MT4): Frequently found on medium to large lathes and drilling machines, suitable for larger tools and moderate load machining applications.
o Large sizes (MT5 to MT7): Primarily used on heavy-duty lathes, industrial-grade drilling machines, or specialized large machinery, capable of withstanding higher torque and heavy loads.
2.Self-locking Design Morse tapers feature a self-locking mechanism, making the tool holders resistant to slipping once inserted; some sizes even do not require screws for fixation.
3.High Concentricity The design ensures excellent axial alignment, suitable for high-speed rotation and high-precision machining.
4.Easy Removal Tools can be ejected from the taper socket using a drift pin or knockout bar.

Common Applications of Morse Taper Tool Holders
•Drilling Machines and Vertical Drilling Machines: For securely holding drills, reamers, and other cutting tools to achieve high-precision holes.
•Lathe Tailstocks: For mounting centers, drills, and supporting workpieces during hole machining.
•Milling Machines and Machining Centers: Through adapter sleeves or dedicated tool holders, enabling quick tool changes and efficient machining.
•Machine Tool Spindles: Serve as the interface connecting the cutting tool and spindle, enabling power transmission and precise positioning.
Additionally, Morse taper tool holders are often combined with other tool holder systems (such as BT, HSK, CAT) to meet diverse machining requirements.
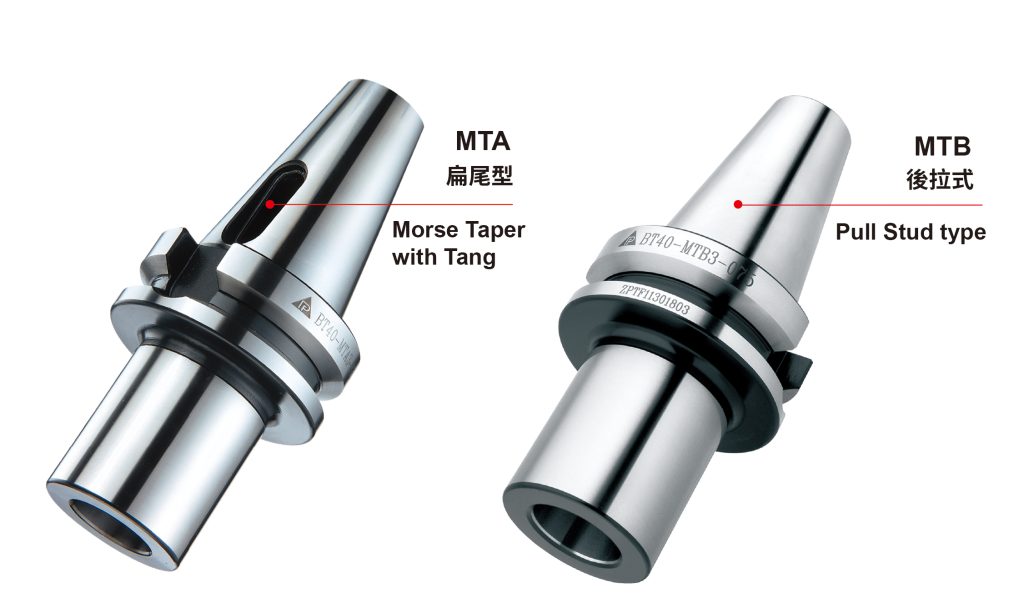

For more detailed specifications of Morse taper tool holders, see types such as MTA and MTB.MTA,MTB